What Is Calcium's Atomic Mass
Atomic Number of Calcium
Calcium is a element with diminutive number xx which means there are twenty protons and 20 electrons in the atomic construction. The chemical symbol for Calcium is Ca.
Since the number of electrons is responsible for the chemic behavior of atoms, theatomic number identifies the various chemical elements.
How does the atomic number determine the chemical behavior of atoms?
Diminutive Mass of Calcium
Atomic mass of Calcium is 40.078 u.
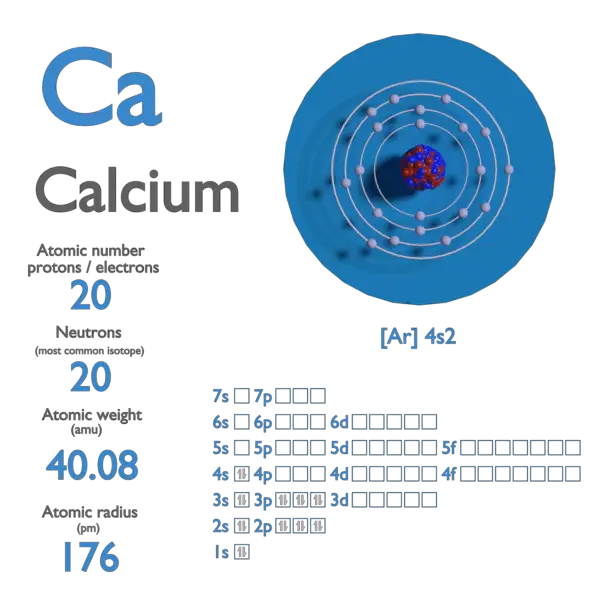
Note that each element may contain more isotopes. Therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occurring isotopes and their abundance.
The unit of measure for mass is theatomic mass unit (amu). One diminutive mass unit is equal to ane.66 10 10-24 grams. One unified atomic mass unit isapproximately the mass of one nucleon (either a single proton or neutron) and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.
For12C, the atomic mass is exactly 12u, since the diminutive mass unit is defined from it. For other isotopes, the isotopic mass usually differs and is usually inside 0.1 u of the mass number. For example, 63Cu (29 protons and 34 neutrons) has a mass number of 63, and an isotopic mass in itsnuclear ground state is 62.91367 u.
There are two reasons for the departure between mass number and isotopic mass, known as the mass defect:
- Theneutron is slightly heavier than theproton. This increases the mass of nuclei with more neutrons than protons relative to the atomic mass unit of measurement scale based on12C with equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
- The nuclear binding energy varies betwixt nuclei. A nucleus with greater binding energy has lower full energy, and therefore alower mass co-ordinate to Einstein'south mass-energy equivalence relationEast =mc 2. For 63Cu, the atomic mass is less than 63, so this must be the ascendant factor.
The atomic mass number determines especially the atomic mass of atoms. The mass number is different for each different isotope of a chemical chemical element.
How does the atomic mass determine the density of materials?
Density of Calcium
Density of Calcium is 1.55g/cm3 .

Typical densities of various substances at atmospheric pressure.
Density is defined equally themass per unit volume. It is anintensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided past volume:
ρ = g/V
In other words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided past the total volume (5) occupied by that substance. The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/thouiii ). The Standard English unit ispounds mass per cubic human foot (lbm/ftthree ).
Encounter too: What is Density
See as well: Densest Materials of the Earth

Calcium – Backdrop Summary
| Chemical element | Calcium |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | xx |
| Symbol | Ca |
| Chemical element Category | Alkaline Earth Metal |
| Phase at STP | Solid |
| Diminutive Mass [amu] | 40.078 |
| Density at STP [g/cm3] | one.55 |
| Electron Configuration | [Ar] 4s2 |
| Possible Oxidation States | +2 |
| Electron Affinity [kJ/mol] | 2.37 |
| Electronegativity [Pauling calibration] | one |
| 1st Ionization Energy [eV] | half-dozen.1132 |
| Year of Discovery | 1808 |
| Discoverer | Davy, Sir Humphry |
| Thermal properties | |
| Melting Indicate [Celsius scale] | 842 |
| Boiling Point [Celsius scale] | 1484 |
| Thermal Electrical conductivity [Due west/m Yard] | 200 |
| Specific Oestrus [J/thou K] | 0.63 |
| Heat of Fusion [kJ/mol] | 8.54 |
| Heat of Vaporization [kJ/mol] | 153.iii |
Calcium in Periodic Table
| Hydrogen ane H | Helium 2 He | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lithium three Li | Beryllium iv Exist | Boron 5 B | Carbon 6 C | Nitrogen 7 North | Oxygen viii O | Fluorine 9 F | Neon 10 Ne | ||||||||||||
| Sodium 11 Na | Magnesium 12 Mg | Aluminium 13 Al | Silicon 14 Si | Phosphorus xv P | Sulfur 16 Due south | Chlorine 17 Cl | Argon 18 Ar | ||||||||||||
| Potassium xix G | Calcium xx Ca | Scandium 21 Sc | Titanium 22 Ti | Vanadium 23 Five | Chromium 24 Cr | Manganese 25 Mn | Atomic number 26 26 Fe | Cobalt 27 Co | Nickel 28 Ni | Copper 29 Cu | Zinc thirty Zn | Gallium 31 Ga | Germanium 32 Ge | Arsenic 33 Equally | Selenium 34 Se | Bromine 35 Br | Krypton 36 Kr | ||
| Rubidium 37 Rb | Strontium 38 Sr | Yttrium 39 Y | Zirconium forty Zr | Niobium 41 Nb | Molybdenum 42 Mo | Technetium 43 Tc | Ruthenium 44 Ru | Rhodium 45 Rh | Palladium 46 Pd | Silver 47 Ag | Cadmium 48 Cd | Indium 49 In | Tin 50 Sn | Antimony 51 Sb | Tellurium 52 Te | Iodine 53 I | Xenon 54 Xe | ||
| Caesium 55 Cs | Barium 56 Ba | Lanthanum 57 La | | Hafnium 72 Hf | Tantalum 73 Ta | Tungsten 74 Westward | Rhenium 75 Re | Osmium 76 Os | Iridium 77 Ir | Platinum 78 Pt | Golden 79 Au | Mercury fourscore Hg | Thallium 81 Tl | Lead 82 Pb | Bismuth 83 Bi | Polonium 84 Po | Astatine 85 At | Radon 86 Rn | |
| Francium 87 Fr | Radium 88 Ra | Actinium 89 Ac | | Rutherfordium 104 Rf | Dubnium 105 Db | Seaborgium 106 Sg | Bohrium 107 Bh | Hassium 108 Hs | Meitnerium 109 Mt | Darmstadtium 110 Ds | Roentgenium 111 Rg | Copernicium 112 Cn | Nihonium 113 Nh | Flerovium 114 Fl | Moscovium 115 Mc | Livermorium 116 Lv | Tennessine 117 Ts | Oganesson 118 Og | |
| | Cerium 58 Ce | Praseodymium 59 Pr | Neodymium 60 Nd | Promethium 61 Pm | Samarium 62 Sm | Europium 63 Eu | Gadolinium 64 Gd | Terbium 65 Tb | Dysprosium 66 Dy | Holmium 67 Ho | Erbium 68 Er | Thulium 69 Tm | Ytterbium 70 Yb | Lutetium 71 Lu | |||||
| | Thorium 90 Th | Protactinium 91 Pa | Uranium 92 U | Neptunium 93 Np | Plutonium 94 Pu | Americium 95 Am | Curium 96 Cm | Berkelium 97 Bk | Californium 98 Cf | Einsteinium 99 Es | Fermium 100 Fm | Mendelevium 101 Md | Nobelium 102 No | Lawrencium 103 Lr | |||||
–
–
–
What Is Calcium's Atomic Mass,
Source: https://www.nuclear-power.com/calcium-atomic-number-mass-density/
Posted by: floreswheed1992.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Calcium's Atomic Mass"
Post a Comment